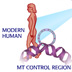
Human/Neandertal/Chimp mutation evoluton tree
Mutations in our DNA can be used to trace the relationships between different populations and species.
species evolution,chimp,mutations,mutation,populations,dna,relationships
- ID: 15608
- Source: DNALC.DNAi
Related Content
15980. Accumulating mutations
Mutations are the grist of evolution, and have accumulated in our DNA over time. When populations separate, each group accumulates their own unique set of DNA mutations.
16611. Problem 27: Mutations are changes in genetic information.
Use mutations to measure human evolution.
16094. Human, Neandertals, Chimpanzee
Phylogenetic relationships of modern humans, Neandertals, and chimps.
16608. Video 27: Svante Paabo, clip 2
What molecular genetics tells us about the Neandertal relationship to modern humans.
16587. Concept 27: Mutations are changes in genetic information.
Some mutations are starting points for evolution, others are responsible for disease.
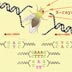
15617. DNA nucleotide mutation
A single DNA nucleotide undergoes a "point" mutation, changing an A to a T.
16095. Chimp, Human, Neandertal HVR1
Variation between mtDNA (HVR1) samples from chimp, Neandertal and human.
15529. Radiation can cause DNA mutations, 3D animation with narration
Mutations and the molecular clock.
15979. A mitochondrial DNA sequence
Human mitochondrial DNA is 16,569 base pairs in length.
15619. Human / Chimp mtDNA tree comparison
Comparison of genetic diversity in humans and chimpanzees, using sequences from 811 humans and 332 chimps.