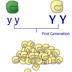
Some genes are dominant.

Mendel identifies dominant and recessive genes.
Mendel believed that genes behave like atoms that compose a pure substance. Genes can combine in various ways, but always maintain their distinct identities. For example, in a cross between two pure-bred parents with different traits like seed color, the hybrid offspring would have both the gene alternates for green and yellow seed color. Why then do offspring from such a cross have only yellow seeds? Mendel proposed that although both gene alternates are present, there is no blending of color because the gene alternate for yellow is "dominant" over the gene alternate for green. The dominant trait is seen whenever a single copy of its gene is inherited. When he crossed the hybrid offspring, green seeds reappeared in the next generation. Mendel reasoned that the "recessive" green trait is shown only when a copy of the recessive gene form is inherited from each parent.
dominant trait, recessive trait, hybrid, offspring,pure-bred parents.seed color, distinct identities,gene,gene alternates,mendel, next generation
- ID: 16181
- Source: DNALC.DNAFTB
Related Content
16190. Some genes are dominant.
DNAFTB Problem 4: Cross pure-bred pea plants to identify dominant flower color.
16168. Problem 2: Genes come in pairs
Repeat Mendel's experiments with an eighth trait.
16182. Some genes are dominant.
DNAFTB Animation 4: Gregor Mendel explains the rules of inheritance.
16153. Concept 2: Genes Come in Pairs
Mendel deduced that pure-bred parents have two copies of the same gene for each trait.
16169. Concept 3: Gene's don't blend.
Mendel discovered that pure-bred plants did not produce offspring with blended traits.
16170. Genes don't blend.
DNAFTB Animation 3: Gregor Mendel explains that breeding short and tall pea plants didn't produce a medium-sized plant.
16180. Genes don't blend.
DNAFTB Problem 3:Breed pea plants to observe flower color.
16151. Biography 1: Gregor Mendel (1822-1884)
Father of Genetics
16191. Concept 5: Genetic inheritance follows rules.
Different gene combinations result in different dominant/recessive ratios in offspring.
16313. Problem 12: Evolution begins with the inheritance of gene variations.
DNAFTB Problem 12:Explore "hybrid vigor."