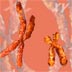
mys inserted in chromosomes
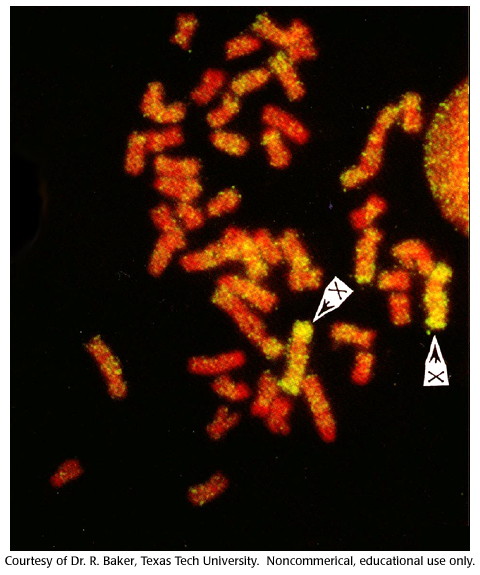
Repetitive DNA can have preferred insertion sites. In this example, yellow represents the distribution of mys (a type of LINE) over a mouse genome where chromosomes are orange. There are more mys inserted in the sex (X) chromosomes.
mys, x chromosomes, repetitive dna, mouse genome, sex x, insertion
- ID: 16660
- Source: DNALC.DNAFTB
Related Content
15520. DNA is organized into 46 chromosomes including sex chromosomes, 3D animation
DNA is organized into 46 chromosomes including sex chromosomes, 3D animation
15419. X chromosome: gene for color blindness, Matt Ridley
Matt Ridley talks about X chromosome: gene for color blindness.
16092. Human genome
The human genome following NCBI.
16657. Some DNA does not encode protein.
DNAFTB Animation 31: Roy Britten presents his work with David Kohne on repetitive DNA and its evolutionary origins.
16249. Specialized chromosomes determine sex.
DNAFTB Concept 9: Study of meiosis revealed the chromosomal basis of sex.
15940. What is color blindness?
The two genes that produce red and green light-sensitive proteins are located on the X chromosome.
16811. Concept 39: A genome is an entire set of genes.
Our genome is a set of long DNA molecules containing tens of thousands of genes.
16261. Specialized chromosomes determine sex.
DNAFTB Problem 9: Try your hand at sex determination.
1241. Breakpoints
Professor David Porteous explains that breakpoints in the genome are locations on a chromosome where DNA might get deleted, inverted, or swapped around.
16250. Specialized chromosomes determine sex.
DNAFTB Animation 9: Nettie Stevens and Edmund Wilson explain how biological sex is determined by special chromosomes.