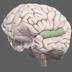
Wernicke's Area
Wernicke's area is a functionally defined structure that is involved in language comprehension.
Wernicke's area is a functionally defined structure that is involved in language comprehension. In about 97% of humans (including a large majority of left–handers) major language functions are contained in the left hemisphere of the brain and for most people, Wernicke's area is lateralized to the left side. It takes its name from Carl Wernicke, who worked with language-impaired patients to distinguish separate regions for language comprehension from production.
wernicke, wernickes, brain, language comprehension, lateralization
- ID: 1998
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2239. Language
An overview of language-related content on Genes to Cognition Online.
2121. Superior Temporal Gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus contain is responsible for processing sounds. It includes Wernicke's area, which is the major area involved in the comprehension of language.
1114. Temporal Lobe Hallucinations
Dr. Sukhi Shergill discusses the role the temporal lobe plays in hallucinations.
2098. Broca's Area
Broca's area is a functionally defined structure in the left frontal lobe of most humans. It is involved mainly in producing speech, writing, and also in language processing and comprehension.
832. White Matters
Only quite recently have neuroscientists begun to understand the importance of white matter, a long-neglected part of the brain.
2369. The Visual Cortex and Plasticity
Doctor Gul Dolen describes how the brain learns through plasticity, making particular reference to the visual cortex.
2002. Integrating levels of understanding
Doctor Thomas Insel discusses the importance of understanding behavior on multiple levels and the interactions of genes, cells, and social systems.
883. Treating Autism
Exploring the possiblities of 'bringing back' the brain of a child with autism.
1180. Cortical Asymmetry - Left Brain, Right Brain
Professor Daniel Geschwind explains that cortical asymmetry refers to differences between the right and left side of the brain. This relates to gene expression.
15578. Language (words, signs, symbols, heiroglyphs)
Language: image collage of heiroglyphs, sign language, and books.