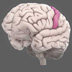
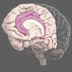
Dentate Gyrus
The dentate gyrus is one of the few regions in the brain where adult neurogenesis has been confirmed. It may play an important role in translating neural codes for creating memories.
The hippocampal formation has three regions, which are highly interconnected: the dentate gyrus, CA3, and CA1. It is one of the very few regions in the brain where adult neurogenesis (development of new neurons) has been confirmed. The dentate gyrus may play an important role in translating complex neural codes from cortical areas into simper code that can be used by the hippocampus to form new memories.
dentate gyrus, brain, neurogenesis, neural, code
- ID: 2107
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
848. Exercise-induced Neurogenesis
Evidence in humans that a structured exercise training program increases neurogenesis.
2207. Blood-brain barrier
Professor Bruce McEwen describes the blood-brain barrier, which prevents most proteins from accessing the brain. Selective proteins can cross the barrier, instigating processes such as neurogenesis.
838. Stem Cell Possibilities
Research continues to show that stem cells could be harnessed for therapeutic purposes.
2115. Somatosensory Cortex
The somatosensory cortex integrates sensory information from the body, producing a map similar to that of the primary motor cortex.
2108. Entorhinal Cortex
The entorhinal cortex plays a major role in memory formation. Two major connections from the entorhinal area input to the hippocampus and are important to pre–processing memory information.
859. Neurogenesis and Timing
New neurons in the hippocampus may remember the timing of events.
2106. Cingulate Gyrus
An important part of the limbic system, the cingulate gyrus helps regulate emotions and pain. It is also involved in predicting and avoiding negative consequences.
2096. Cerebellum
The cerebellum monitors and regulates motor behavior, particularly automatic movements. It contains more neurons than the rest of the brain and is a site of neurogenesis.
1161. Neurogenesis Instability
Professor Fred Gage explains that neurogenesis is an unstable process and is highly regulated by the environment.
1997. Learning and memory
Learning and memory are two intimately linked cognitive processes that stem from interactions with the environment (experience).