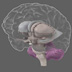
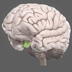
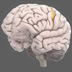
Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia comprise a group of structures that regulate the initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture.
The basal ganglia comprise a group of structures that regulate the initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture. They are strongly connected to other motor areas in the brain and link the thalamus with the motor cortex. The basal ganglia are also involved in cognitive and emotional behaviors and play an important role in reward and reinforcement, addictive behaviors and habit formation.
basal ganglia, brain, motor, emotional behaviors, eye movements
- ID: 2092
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
833. Basal Ganglia and Learning
The basal ganglia, a group of interconnected brain areas located deep in the cerebral cortex, have proved to be at work in learning, the formation of good and bad habits, and some psychiatric and addictive disorders.
1154. Basal Ganglia - Primary Functions
Professor Trevor Robbins discusses the function of a set of structures called the basal ganglia, which seem to be involved in response selection.
2096. Cerebellum
The cerebellum monitors and regulates motor behavior, particularly automatic movements. It contains more neurons than the rest of the brain and is a site of neurogenesis.
851. Developing Mirror Neurons
Mirror neurons provide an important shortcut to learning new movements.
2119. Perirhinal Cortex
The perirhinal cortex plays an important role in object recognition and in storing information (memories) about objects. It is highly connected to other brain structures.
880. Relatives' Brains and Autism
Brain scans of close relatives of children with autism reveal clear abnormalities that parallel those seen in autism.
2102. Motor Cortex
The primary motor cortex is critical to initiating motor movements. Areas of the motor cortex correspond precisely to specific body parts.
1254. Schizophrenia - Motor Control
Professor David Lewis explains that schizophrenic individuals can have coordination problems, which may relate to impaired neural circuits.
1278. Aplysia and Learning
Professor Eric Kandel discusses the attributes that make Aplysia, a type of sea slug, an ideal model for studying learning and memory.
849. Hippocampus and Memory (2)
The potential gains of improving or therapeutically altering memory are compelling, but ethical considerations are imperative.