Motor Cortex
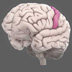
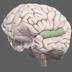
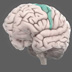
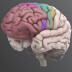
The primary motor cortex is critical to initiating motor movements. Areas of the motor cortex correspond precisely to specific body parts.
The primary motor cortex (also known as M1) is critical to initiating motor movements. Areas of the motor cortex correspond precisely to specific body parts. For example, leg movements map to the part of the motor cortex closest to the midline. Not all body parts are equally represented by surface area or cell density – representations of the arm hand motor area occupy the most space in the motor cortex (unsurprising given their importance to human behavior). Similarly, representations in the motor cortex can become relatively large or small with practice/training.
primary, motor, cortex, m1, movement, map
- ID: 2102
- Source: DNALC.G2C
Related Content
2115. Somatosensory Cortex
The somatosensory cortex integrates sensory information from the body, producing a map similar to that of the primary motor cortex.
2121. Superior Temporal Gyrus
The superior temporal gyrus contain is responsible for processing sounds. It includes Wernicke's area, which is the major area involved in the comprehension of language.
2101. Premotor Cortex
The premotor cortex is involved in preparing and executing limb movements and coordinates with other regions to select appropriate movements.
2092. Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia comprise a group of structures that regulate the initiation of movements, balance, eye movements, and posture.
1129. Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is part of the cerebral cortex and is the largest of the brain's structures. It is the main site of so–called 'higher' cognitive functions.
2094. Brain Stem
The brain stem consists of a group of structures, including the pons, medulla oblongata, and midbrain. It controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
1971. Mirror neurons: brain regions
Professor Christian Keysers explains that mirror neurons can be found in many regions of the brain.
1128. Parietal Lobe
The parietal cortex plays an important role in integrating information from different senses to build a coherent picture of the world.
851. Developing Mirror Neurons
Mirror neurons provide an important shortcut to learning new movements.
854. Einstein's Brain
Einstein's brain, was it different to yours?